|
 Changing Administrative Counties Changing Administrative Counties
Producers who wish to transfer their farm records to a different
administrative county for Fiscal Year (FY) 2016 must file a
request no later than August 1, 2016. Restrictions do apply when
transferring to an office other than the county in which the
land is physically located. Contact your local FSA office for
more information.
USDA Financial Assistance Available to Help Organic Farmers
Create Conservation Buffers
USDA is assisting organic farmers with the cost of establishing
up to 20,000 acres of new conservation buffers and other
practices on and near farms that produce organic crops.

The financial assistance is available from the USDA Conservation
Reserve Program (CRP), a federally funded voluntary program that
contracts with agricultural producers so that environmentally
sensitive land is not farmed or ranched, but instead used for
conservation benefits. CRP participants establish long-term,
resource-conserving plant species, such as approved grasses or
trees (known as “covers”) to control soil erosion, improve water
quality and develop wildlife habitat. In return, FSA provides
participants with rental payments and cost-share assistance.
Contract duration is between 10 and 15 years.
For conservation buffers, funds are available for establishing
shrubs and trees, or supporting pollinating species, and can be
planted in blocks or strips. Interested organic producers can
offer eligible land for enrollment in this initiative at any
time.
Other USDA FSA programs that assist organic farmers include:
- The Noninsured Crop Disaster Assistance Program that
provides financial assistance for 55 to 100 percent of the
average market price for organic crop losses between 50 to
65 percent of expected production due to a natural disaster.
- Marketing assistance loans that provide interim
financing to help producers meet cash flow needs without
having to sell crops during harvest when market prices are
low, and deficiency payments to producers who forgo the loan
in return for a payment on the eligible commodity.
- A variety of loans for operating expenses, ownership or
guarantees with outside lenders, including streamlined
microloans that have a lower amount of paperwork.
Farm Storage Facility Loans that provide low-interest
financing to build or upgrade storage facilities for organic
commodities, including cold storage, grain bins, bulk tanks
and drying and handling equipment.
- Services such as mapping farm and field boundaries and
reporting organic acreage that can be provided to a farm’s
organic certifier or crop insurance agent.

Visit
www.fsa.usda.gov/organic to learn more about how FSA
can help organic farmers. For an interactive tour of CRP success
stories, visit www.fsa.usda.gov/CRPis30 or follow #CRPis30 on
Twitter. To learn more about FSA programs visit a local FSA
office or www.fsa.usda.gov. To find your local FSA office, visit
http://offices.usda.gov.
Maintaining the Quality of Loaned Grain
Bins are ideally designed to hold a level volume of grain. When
bins are overfilled and grain is heaped up, airflow is hindered
and the chance of spoilage increases.
Producers who take out marketing assistance loans and use the
farm-stored grain as collateral should remember that they are
responsible for maintaining the quality of the grain through the
term of the loan.
Conduct USDA Business Online by Creating an
e-authentication Account
The Internet allows you, the customer, access to USDA
information 24 hours a day, seven days a week. You can fill
out and submit electronic forms (eForms) any time of the day
or night from anywhere you have Internet access. This new
service delivery option allows you to complete and file your
own forms or applications online, because your signature is
already electronically "on file."
Information submitted to the Federal Government remains safe
and secure because every customer has a unique User ID and
password; only authorized USDA employees can access your
information. It's safe, saves paper, saves a visit to your
local USDA Service Center and provides electronic tracking
of all your USDA transactions.
How to Sign Up for eAuth :
Begin the process by reviewing the information at the USDA
Website https://www.eauth.usda.gov. This website describes
the services available for Level 1 and Level 2 Accounts.
Level 1 and Level 2 accounts require that you have an email
address so you can register, create a customer profile, and
be able to respond to a confirmation email. Level 1 Accounts
do not require you to provide proof of your identity at a
local USDA Service Center. Level 1 Accounts provide limited
access to certain USDA Web site portals that require no
authentication or authorization. A Level 2 Account does
require a visit to a USDA Service Center with proof of your
identity. That is because a Level 2 account allows you
access to complete and submit documents and forms
electronically.

LEVEL 1 ACCOUNT
STEP 1. To obtain a Level 1 Account, you may self-register
online at www.eauth.egov.usda.gov.
Scroll down and click on the button that says “Sign Up for a
Level 1 Account.” Complete the brief customer profile.
STEP 2. You will receive a confirmation email, and you must
respond to it within 7 days to activate your account.
LEVEL 2 ACCOUNT
STEP 1. To obtain a Level 2 Account, you must complete an 18
question customer profile and prove your identity by
presenting state or federal photo ID at a local USDA Service
Center. Go to www.eauth.egov.usda.gov, scroll down and click
on “Sign Up for a Level 2 Account.” Complete your customer
profile, which includes designating your user ID and
password created by you, contact information and email
information. The data you enter in your customer profile
must match the data on the document you use as
identification at your local USDA Service Center. Example:
Your first and last names and address must match the
government-issued photo ID you plan to use to prove your
identity. Identify proof can only be verified by one of the
following documents: Current State Driver’s License, State
Photo ID, US Military ID, or United States Passport.
STEP 2. After completing your customer profile and
submitting it online, you will receive a confirmation email,
and you must respond to it within 7 days to activate your
account.
STEP 3. Then you must complete the “Identify Proofing”
process by visiting a local USDA Service Center. You will be
required to present the eligible photo ID to an USDA
employee who will verify your identity and enter the
expiration date of the ID document used.
STEP 4. The USDA employee then will update your customer
profile to a Level 2 Account. You will have access to USDA
online applications and forms within one hour of your
account being updated.

You now have access to complete and submit documents and
forms electronically. USDA continues to update and make more
forms and programs available electronically.
2016 Acreage Reporting Date
Producers who file accurate and timely reports for all crops
and land uses, including failed acreage can prevent the
potential loss of FSA program benefits. Please pay close
attention to the acreage reporting dates below, as some
dates have changed.
In order to comply with FSA program eligibility
requirements, all producers are encouraged to visit their
local County FSA office to file an accurate crop
certification report by the applicable deadline.
The following 2016 acreage reporting dates are applicable
for Illinois:
- September 30, 2015 - aquaculture, Christmas trees,
turfgrass sod, floriculture
- December 15, 2015 - perennial forage (with an
intended use of haying or grazing),
fall-seeded small grains
- January 2, 2016 - honey
- January 15, 2016 - apples, asparagus, blueberries,
caneberries, cherries, grapes,
nectarines, peaches, pears, plums, strawberries
- June 15, 2016 - cucumbers (planted 5/1 – 5/31) in
Gallatin, Lawrence, and White
Counties
- July 15, 2016 - cabbage (planted 3/15 – 5/31),
perennial forage (with an intended
use of cover only, green manure, left standing, or seed
and all other
crops
- August 15, 2016 - cabbage (planted 6/1 – 7/20)
- September 15, 2016 - cucumbers (planted 6/1 – 8/15)
in Gallatin, Lawrence, and White Counties

The following exceptions apply to the above acreage
reporting dates:
- If the crop has not been planted by the above
acreage reporting date, then the acreage must be
reported no later than 15 calendar days after planting
is completed.
- If a producer acquires additional acreage after the
above acreage reporting date, then the acreage must be
reported no later than 30 calendars days after purchase
or acquiring the lease. Appropriate documentation must
be provided to the county office.
- If a perennial forage crop is reported with the
intended use of “cover only,” “green manure,” “left
standing,” or “seed,” then the acreage must be reported
by July 15, 2016. Noninsured Crop Disaster Assistance
Program (NAP) policy holders should note that the
acreage reporting date for NAP covered crops is the
earlier of the dates listed above or 15 calendar days
before grazing or harvesting of the crop begins.
For questions regarding crop certification and crop loss
reports, please contact your local County FSA office.
If filing for prevented planting, an acreage report and
CCC-576 must be filed within 15 calendar days of the final
planting date for the crop.
Reporting Organic Crops
Producers who want to use the Noninsured Crop Disaster
Assistance Program (NAP) organic price and selected the
"organic" option on their NAP application must report their
crops as organic.
When certifying organic acres, the buffer zone acreage must
be included in the organic acreage.
[to top of second column] |

Producers must also provide a current organic plan, organic
certificate or documentation from a certifying agent indicating an
organic plan is in effect. Documentation must include:
- name of certified individuals
- address
- telephone number
- effective date of certification
- certificate number
- list of commodities certified
- name and address of certifying agent
- a map showing the specific location of each field of
certified organic, including the buffer zone acreage
Certification exemptions are available for producers whose annual
gross agricultural income from organic sales totals $5,000 or less.
Although exempt growers are not required to provide a written
certificate, they are still required to provide a map showing the
specific location of each field of
certified organic, transitional and buffer zone acreage.
For questions about reporting organic crops, contact your local FSA
office. To find your local office, visit
http://offices.usda.gov.

Emergency Assistance for Livestock, Honeybees and Farm-Raised
Fish Program (ELAP)
ELAP provides emergency assistance to eligible producers of
livestock, honeybees and farm-raised fish that have losses due to
disease, adverse weather, or other conditions, such as blizzards and
wildfires.
Producers who suffer eligible livestock, honeybee, or farm-raised
fish losses from October 1, 2015 to September 30, 2016 must file:
- A notice of loss the earlier of 30 calendar days of when the
loss is apparent or by November 1, 2016
- An application for payment by November 1, 2016
The Farm Bill caps ELAP disaster funding at $20 million per
federal fiscal year.
To view ELAP Farm-Raised Fish, ELAP for Livestock or ELAP for
Honeybee fact sheets visit the FSA fact sheet web page at
www.fsa.usda.
gov/factsheets.
Loan Servicing
There are options for Farm Service Agency loan customers during
financial stress. If you are a borrower who is unable to make
payments on a loan, contact your local FSA Farm Loan Manager to
learn about the options available to you.
MAL’s Available for Crop Years 2015-2018
The 2014 farm bill authorizes 2014-2018 crop year Marketing
Assistance Loans (MAL’s).
MALs provide financing and marketing assistance for wheat, feed
grains, soybeans, and other oilseeds, pulse crops, wool and honey.
MALs provide producers interim financing after harvest to help them
meet cash flow needs without having to sell their commodities when
market prices are typically at harvest-time lows.
FSA is now accepting requests for 2015 crop MALs for all eligible
commodities after harvest.
The 2014 Farm Bill also establishes payment limitations per
individual or entity not to exceed $125,000 annually on certain
commodities for the following program benefits: ARC PLC, marketing
loan gains (MLGs) and LDPs. These payment limitations do not apply
to MAL loan disbursements.

For more information and additional eligibility requirements, please
visit a nearby USDA Service Center or FSA’s website
www.fsa.usda.gov.
Livestock Indemnity Program (LIP)
The Livestock Indemnity Program (LIP) provides assistance to
eligible producers for livestock death losses in excess of normal
mortality due to an extreme or abnormal adverse weather event and/or
attacks by animals reintroduced into the wild by the federal
government or protected by federal law. LIP compensates livestock
owners and contract growers for livestock death losses in excess of
normal mortality due to adverse weather, including losses due to
hurricanes, floods, blizzards, wildfires, extreme heat or extreme
cold.
For 2016, eligible losses must occur on or after Jan. 1, 2016, and
before December 31, 2016. A notice of loss must be filed with FSA
within 30 days of when the loss of livestock is apparent.
Participants must provide the following supporting documentation to
their local FSA office no later than 30 calendar days after the end
of the calendar year for which benefits are requested:
- Proof of death documentation
- Copy of growers contracts
- Proof of normal mortality documentation
Guaranteed Loan Program
FSA guaranteed loans allow lenders to provide agricultural credit to
farmers who do not meet the lender's normal underwriting criteria.
Farmers and ranchers apply for a guaranteed loan through a lender,
and the lender arranges for the guarantee. FSA can guarantee up to
95 percent of the loss of principal and interest on a loan.
Guaranteed loans can be used for both farm ownership and operating
purposes.
Guaranteed farm ownership loans can be used to purchase farmland,
construct or repair buildings, develop farmland to promote soil and
water conservation or to refinance debt.
Guaranteed operating loans can be used to purchase livestock, farm
equipment, feed, seed, fuel, farm chemicals, insurance and other
operating expenses.
FSA can guarantee farm ownership and operating loans up to
$1,399,000. Repayment terms vary depending on the type of loan,
collateral and the producer's ability to repay the loan. Operating
loans are normally repaid within seven years and farm ownership
loans are not to exceed 40 years.
Please contact your lender or local FSA farm loan office for more
information on guaranteed loans.

Unauthorized Disposition of Grain
If loan grain has been disposed of through feeding, selling or any
other form of disposal without prior written authorization from the
county office staff, it is considered unauthorized disposition. The
financial penalties for unauthorized dispositions are severe and a
producer’s name will be placed on a loan violation list for a
two-year period. Always call before you haul any grain under loan.
Value Added Producer Grants Available
Application Deadline is July 1, 2016
Approximately $44 million in funding is available to help
agricultural producers enter into value-added activities for FY
2016.
The grants help agricultural producers increase their income by
expanding marketing opportunities, creating new products or
developing new uses for existing products.
The maximum grant award is $250,000 for working capital and $75,000
for planning. Planning grants can be used to facilitate economic
planning activities to determine the viability of a value-added
venture, and may include costs for an independent feasibility study
and development of a marketing and business plan. Working capital
grants are used for operational costs directly related to processing
and/or marketing of the value-added product.
USDA Rural Development has provided funding for a wide variety of
value-added agriculture projects involving locally produced and
marketed foods. These include cheese, wine, reduced-cholesterol
dairy products, produce, packaged poultry, pork and beef products,
and a variety of processed or prepared foods from locally grown
fruits and vegetables.

Applications must be submitted to USDA Rural Development by July 1,
2016, in order to be considered for funding.
For more information contact Matthew Harris at 217-403-6211 or
Matthew.harris@il.usda.gov
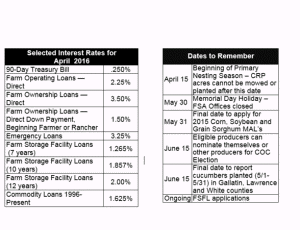
DATES TO REMEMBER
Illinois Farm
Service Agency
3500 Wabash Ave.
Springfield, IL 62711
www.fsa.usda.gov/il
State
Committee:
Jill Appell - Chair
Brenda Hill - Member
Jerry Jimenez - Member
Joyce Matthews - Member
Gordon Stine - Member
State
Executive Director:
Scherrie V. Giamanco
Executive
Officer:
Rick Graden
Administrative Officer:
Dan Puccetti
Division
Chiefs:
Doug Bailey
Jeff Koch
Stan Wilson
Please contact
your local FSA Office for questions specific to your operation or
county.
 |