|
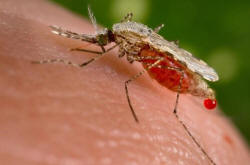 In
the lab: six innovations scientists hope will end malaria In
the lab: six innovations scientists hope will end malaria
 Send a link to a friend
Send a link to a friend
[June 08, 2016]
By Katy Migiro
ARUSHA, Tanzania (Thomson Reuters
Foundation) - After being abandoned as too ambitious in 1969, global
plans to eliminate malaria are back on the agenda, with financial
backing from the world's richest couple, Bill and Melinda Gates, and
U.S. President Barack Obama.
|
|
 The Gateses aim to eradicate malaria by 2040 by doubling funding
over the next decade to support the roll out of new products to
tackle rising drug resistance against the disease. The Gateses aim to eradicate malaria by 2040 by doubling funding
over the next decade to support the roll out of new products to
tackle rising drug resistance against the disease.
Their goal of permanently ending transmission of the disease between
humans and mosquitoes is more ambitious than the Sustainable
Development Goal of ending epidemic levels of malaria by 2030.
They are also supporting a push to create the world's first vaccine
against a parasite.
Six innovations scientists are working on are:
* New insecticides: Mosquitoes are becoming resistant to
insecticides used to spray inside homes and in bed nets.
"There is no current insecticide that doesn't show insect-resistance
at the moment," said Jed Stone, a spokesman for the UK-based
Innovative Vector Control Consortium (IVCC).
Indoor spraying of walls with insecticide -- which was used to wipe
out malaria in the United States in the 1940s -- has fallen by 40
percent since 2012 due to resistance to older products and the high
cost of newer ones.

The IVCC is developing three new insecticides for use in indoor
sprays and bed nets that kill insecticide-resistant mosquitoes.
"The insecticides are virtually ready but it will take about five
years to finally develop them," Stone said, adding that this largely
involves registration with regulators.
* A single-dose cure: A pill that would wipe out all parasites in
the body could be available by 2019, the Gates Foundation says.
Human trials of one candidate are planned following successful tests
on mice, published in 2015.
Existing drugs have to be taken for three days with the risk that
people do not finish their medication, contributing to the
development of drug-resistant malaria.
They also only kill parasites at the asexual-stage where they cause
fever but not at the sexual-stage where they are picked up by
mosquitoes in blood.
* Insecticide-treated wall liners: Scientists hope
insecticide-treated wall liners, which look like wallpaper, will be
more effective than spraying people's homes with insecticide every
three to eight months. The wall liners kill mosquitoes that rest on
them and can last for three years.
Tanzania's National Institute for Medical Research is testing wall
liners in 6,000 homes to see if they protect people from malaria.
Results will be published in 2017.
* Insecticide-embedded clothing: American soldiers have been wearing
combat uniforms treated with permethrin, a synthetic insecticide,
since 2010 to protect them against insect-borne diseases.
[to top of second column] |

The U.S. government's Walter Reed Army Institute of Research will
test the effectiveness of treated combat uniforms and repellent
creams in July on Tanzanian soldiers who often catch malaria when
working at night as peacekeepers.
* A vaccine: This is a big one, given vaccines success in
eliminating smallpox, polio and measles in many countries.
More than 30 malaria vaccines are under development.
The Mosquirix vaccine, discovered in 1987, is a decade ahead of
other candidates but, to date, it only halves the number of bouts of
malaria young children suffer.
The World Health Organization is seeking funding for a pilot program
to administer Mosquirix to 400,000 to 800,000 African children. The
results will be used to make a decision on whether to use the
vaccine more widely.
* GM mosquitoes: Scientists have genetically modified (GM)
mosquitoes by adding genes that block the development of the malaria
parasite inside the insect and prevent it from being transmitted to
people.
Scientists have also genetically modified mosquitoes to make them
infertile, so that they die out. But many are cautious about the
unforeseen consequences of this.
"When people imagine a malaria end game scenario, GM mosquito
technology would be incredibly powerful because it doesn't rely on a
robust health system in order to go in and disrupt transmission of
the parasite," said Martin Edlund, chief executive of Malaria No
More, referring to war-torn countries like South Sudan.
The International Center for Journalists and Malaria No More
provided a travel grant for this report

(Reporting by Katy Migiro; Editing by Katie Nguyen; Please credit
the Thomson Reuters Foundation, the charitable arm of Thomson
Reuters, that covers humanitarian news, women’s rights, trafficking,
property rights and climate change. Visit http://news.trust.org to
see more stories.)
[© 2016 Thomson Reuters. All rights
reserved.] Copyright 2016 Reuters. All rights reserved. This material may not be published,
broadcast, rewritten or redistributed.
|