Nigerian artist makes dark skin prosthetics to boost patients'
confidence
 Send a link to a friend
Send a link to a friend
 [January 20, 2020]
By Seun Sanni and Nneka Chile [January 20, 2020]
By Seun Sanni and Nneka Chile
UYO, Nigeria (Reuters) - Michael Sunday is
delighted, if a little stunned, as he admires his new right hand: a
silicone glove-like prosthetic meant to help him return to normal life
after he lost three fingers in a car accident a year ago.
The prosthetic has a hyper-realistic feel and, unusually, is dark in
color, matching perfectly the tone of Sunday's skin.
Most fake body parts available in Nigeria until now have been white, or
made from materials such as wood that also look unrealistic.
"Wow, this is lovely," Sunday said, his voice choked with emotion, as he
looked at the prosthetic for the first time.
"I have my fingers back," said the 22-year-old student, who lost the
thumb and fourth and fifth fingers on his right hand when the car he was
riding in with his parents on Dec. 31, 2018, collided with another
vehicle.

The artist behind the creation is John Amanam, a 32-year-old former
movie special effects expert. He developed an interest in prosthetics
after a family member lost a limb in an accident.
"I became emotional about amputees," said Amanam, who is also Nigerian.
"They had this feeling of discomfort whenever they were around other
people. I saw it as a challenge. If I could give back or solve this
need, it would go a long way to ease that emotional trauma and loss of
confidence," he added.
"I just want them to feel at home and be whole, aesthetically."
So he started making prosthetic fingers, hands, arms, legs and ears in
2017. Depending on the size and complexity of the prosthetic, it takes
three weeks to two months to make one.
Amanam has no formal training in making prosthetics but studied
sculpting as an art student. The pieces are sold for at least 40,000
naira ($111).
[to top of second column]
|
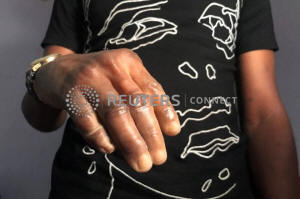
Patient, Michael Sunday, shows his new prosthetic hand at Immortal
Cosmetic Art company, in Uyo, Nigeria January 7, 2020. REUTERS/ Seun
Sanni

His company, Immortal Cosmetic Art, is part of a growing services
industry that has helped Nigeria's economy become the biggest in
Africa.
Amanam said mismatched skin tone makes it more difficult for people
to feel confident with their artificial limbs.
To prepare Sunday's hand, he took measurements, made a plaster cast
and mixed paints on a palette, as any artist would, searching for
the right skin tone. The result was lifelike.
"You rarely find people with black skin prosthetics," Amanam said.
"I want this need to be met within Africa. I want to reach out to
blacks all over the world as well, by making this process
accessible, at an affordable rate."
Sunday, who covers a slight seam between the silicone glove and his
forearm with a watch bearing a wide wristband, is certainly a
satisfied customer.
"I can go about my normal life without people looking at my hand,
without hiding my hands or fear of discrimination or pity," he said.
(Reporting by Seun Sanni and Nneka Chile; Writing by Hugh Bronstein;
Editing by Alexis Akwagyiram and Gareth Jones)
[© 2020 Thomson Reuters. All rights
reserved.] Copyright 2020 Reuters. All rights reserved. This material may not be published,
broadcast, rewritten or redistributed.
Thompson Reuters is solely responsible for this content.
 |