Exclusive-Rotavirus childhood vaccine shortage hits four African
countries
 Send a link to a friend
Send a link to a friend
 [August 12, 2022]
By Jennifer Rigby [August 12, 2022]
By Jennifer Rigby
LONDON (Reuters) - Supplies of a vaccine to
prevent the deadly rotavirus infection in children have either run out
in Kenya, Tanzania, Senegal and Cameroon or are close to doing so,
officials close to the roll-out told Reuters, after disruptions at
drugmaker GSK.
The World Health Organization estimates that up to 200,000 children die
each year of the highly contagious infection, which is the leading cause
globally of severe, dehydrating gastroenteritis in children under the
age of five.
Officials in Kenya, Tanzania, Senegal and Cameroon had no immediate
response to requests for comment from Reuters.
GSK confirmed that there is a shortfall of around 4 million doses of its
Rotarix vaccine this year, with a drop to 42 million from an expected 46
million.
The British drugmaker had already cut its agreed deliveries by 10
million a year for the period 2022-2028, Gavi, the Vaccine Alliance,
said.
GSK acknowledged the fall in supply and said it was pursuing plans to
address the deficit.

"GSK communicated to Gavi earlier this year on manufacturing challenges
leading to an unplanned, short-term drop in Rotarix production for 2022,
for which priority mitigation plans are fully in place," a GSK
spokesperson told Reuters.
GSK did not give any further details on the manufacturing issues or what
plans were in place.
Gavi said that as well as the drop in Rotarix supplies in 2022, there
will also be delays in delivery.
A source close to negotiations between the two parties said they
understood the delays were due to staff absences during the COVID-19
pandemic. GSK did not give further details.
[to top of second column]
|
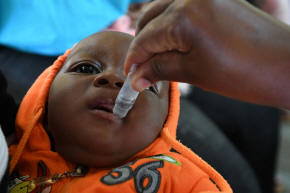
A baby receives the Rotavirus vaccination at Fort Portal Regional
Referral Hospital in Uganda, November 2021. UNICEF/Wamala/Handout
via REUTERS
 IMMUNIZATION BLOW
The supply problems are a blow as national health services scramble
to regain ground lost on routine childhood immunizations during the
coronavirus pandemic.
UNICEF, the children's aid agency within the United Nations, said
COVID-19 disruptions represented the biggest step backwards in a
generation for childhood immunizations.
"It's beyond the normal… and in the environment where countries are
already struggling. It's a really unfortunate time," Andrew Jones,
chief of the vaccine centre at UNICEF's supply division, said about
the rotavirus shortage.
"There will be kids missed," he added in an
interview.
UNICEF works with Gavi to help supply rotavirus vaccines to poorer
countries, alongside national governments. Both organizations said
they were attempting to switch in vaccines made by other
manufacturers, or from countries with spare doses.
Rotarix is given in two oral doses to infants from 6 weeks of age. A
second dose should be given at least 4 weeks after the first, and no
later than 24 weeks, adding to the time pressure on inoculations.
Gavi said there were also delays with another rotavirus vaccine,
Rotavac, manufactured by Bharat Biotech, which were related to
"regulatory procedures", although the problem is not as significant.
Bharat Biotech had no immediate comment.
(Reporting by Jennifer Rigby; Additional reporting by Natalie
Grover; Editing by Alexander Smith)
[© 2022 Thomson Reuters. All rights
reserved.] This material may not be published,
broadcast, rewritten or redistributed.
Thompson Reuters is solely responsible for this content. |