Illinois’ minimum wage to increase to $15 on Jan. 1, completing 6-year
transition
 Send a link to a friend
Send a link to a friend
 [December 27, 2024]
By Ben Szalinski [December 27, 2024]
By Ben Szalinski
The minimum wage in Illinois will increase to $15 an hour on Jan. 1,
completing a six-year transition period since the increase was approved
in 2019.
Beginning New Year’s Day, Illinois workers making minimum wage will see
wages rise by $1 and tipped workers will see their paychecks bump to $9
an hour. Youth workers under 18 who work fewer than 650 hours a year
will have a $13 minimum wage.
The final increase, ending a six-year ramp which began with the minimum
wage rising from $8.25 to $9.25 on Jan. 1, 2020, puts a bow on Gov. JB
Pritzker’s first major legislative victory. He signed the wage increase
in February 2019 about a month after being sworn in for his first term,
checking off a top campaign promise.
“Since day one of my administration, I’ve made it my mission to build an
economy that works for everyone and raising the minimum wage to $15 an
hour fulfills that promise to our working families,” Pritzker said in a
statement. “This increase honors the workers who power our state and
ensures they can better support their families, bringing us closer to a
stronger, more equitable economy for all.”
Illinois will be one of 10 states with a minimum wage of $15 or greater,
according to the National Employment Law Project. Twenty-two other
states are also increasing their wages on Jan. 1.

The minimum wage increase is one of many economic changes that have
happened since 2019, including effects of the pandemic, Illinois Chamber
of Commerce CEO Lou Sandoval told Capitol News Illinois. He said those
have caused businesses to adjust their operations in a variety of ways,
such as increasing automation.
“I think you’re starting to see businesses pivot in terms of how they’re
adjusting,” Sandoval said. “You’re seeing this at the national chains.”
Some restaurants, for example, are “moving away from larger sit-down
areas into grab-and-go.”
Illinois job growth has been slow since October 2019, according to a
November report by the Commission on Government Forecasting and
Accountability. The state has seen a net increase of 28,700 jobs from
October 2019 through October 2024. That’s a growth rate of 0.5%,
compared to the national rate of 4.9%.
The rate of new job postings by businesses at the beginning of the year
will shed some light on how the jump to $15 on Jan. 1 is impacting
business operations, Sandoval said.
To help small businesses with the change, the state provides a tax
credit through 2027 to businesses with 50 or fewer employees for wages
paid to minimum-wage workers.
The 2019 minimum wage law marked the first increase since the wage hit
$8.25 in 2010. Senate Majority Leader Kimberly Lightford, D-Westchester,
introduced a bill to raise it to $15 an hour in 2017 that was passed by
the General Assembly and vetoed by Republican Gov. Bruce Rauner.
Lightford sponsored the initiative again in 2019.
“As a state, we have helped countless workers make ends meet, reduce
financial stress, and provide a more solid foundation for their
futures,” Lightford said in a statement. “The $15 minimum wage is a
testament to our commitment to economic justice and our belief that
everyone who works full time deserves a living wage.”
[to top of second column]
|
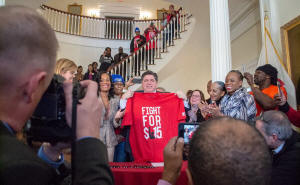
Gov. JB Pritzker holds a shirt commemorating the movement to raise
the minimum wage to $15 after signing the bill on February 20, 2019.
The wage hits $15 in 2025. (Capitol News Illinois photo by Jerry
Nowicki)

The value of a $15 minimum wage, however, has changed since lawmakers
acted in 2019. A person making $8.25 in February 2019 would need to earn
$10.30 today to have the same buying power after inflation, according to
the Consumer Price Index. A $15 hourly wage today has the buying power
that $12.02 had in February 2019. A person would need to make an $18.72
wage today to have the same buying power that $15 had in February 2019.
Top Democrats didn’t say if they will push for new increases.
“As a Senator of 25 years, history has shown my commitment of fighting
to ensure workers are paid a living wage. That commitment still holds
strong today,” Lightford said in an email statement.
Pritzker said he supports ideas that will help workers make more money,
but didn’t commit to supporting any plan to raise the minimum wage
further when pressed about it at a news conference Dec. 11.
“We always are thinking about how do you balance the need for higher
wages with the needs that businesses have to hire people and do it
affordably. But I think we did it the right way when we did it back in
2019,” Pritzker said.
The new $15 wage equates to a 40-hour-per-week annual salary of $31,200
before taxes. That equals the federal government’s poverty level for a
four-person household. The poverty level is $15,060 in a single-person
household.
But according to calculations in a national project by the Massachusetts
Institute of Technology, $15 hourly still doesn’t equate to a “living”
wage in Illinois, based on U.S. Census Bureau cost of living and other
cost estimates provided by federal agencies adjusted for inflation.
A single adult with no children needs a $22.86 hourly salary to make a
living wage in Illinois, while a two-parent household with two working
adults and three children would each need to earn $31.69. In a
two-parent household with one working adult and one child, the worker
needs $36.49 to make a living wage, according to the MIT project.

Inflation is making it hard for workers to benefit from wage increases,
Sandoval said, adding rising wages also cause businesses to raise
prices.
“They might get the wage increase on one side, but their cost of living
goes up accordingly,” Sandoval said.
Capitol News Illinois is
a nonprofit, nonpartisan news service that distributes state government
coverage to hundreds of news outlets statewide. It is funded primarily
by the Illinois Press Foundation and the Robert R. McCormick Foundation. |