|
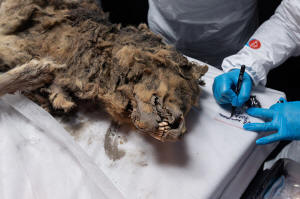
"This is the world's first discovery of a late Pleistocene
predator," said Albert Protopopov, head of the department for
the study of mammoth fauna at the Yakutia Academy of Sciences.
"Its age is about 44,000 years, and there have never been such
finds before," he said.
Sandwiched between the Arctic Ocean and in Russia's Arctic far
east, Yakutia is a vast region of swamps and forests around the
size of Texas, around 95% of which is covered in permafrost.
Winter temperatures in the region have been known to drop to as
low as minus 64 degrees Celsius (-83.2°F)
"Usually, it's the herbivorous animals that die, get stuck in
swamps, freeze and reach us as a whole. This is the first time
when a large carnivore has been found," said Protopopov.
While it's not unusual to find millenia-old animal carcasses
buried deep in permafrost, which is slowly melting due to
climate change, the wolf is special, Protopopov said.
"It was a very active predator, one of the larger ones. Slightly
smaller than cave lions and bears, but a very active, mobile
predator, and it was also a scavenger," he added.
For Artyom Nedoluzhko, development director of the paleogenetics
laboratory at the European University of St Petersburg, the
wolf's remains offer a rare insight into the Yakutia of 44,000
years ago.
"The main goal is to understand what this wolf fed on, who it
was, and how it relates to those ancient wolves that inhabited
the northeastern part of Eurasia," he said.
(Reporting by Reuters; Writing by Felix Light; Editing by Miral
Fahmy)
[© 2024 Thomson Reuters. All rights
reserved.]
Copyright 2022 Reuters. All rights reserved. This material may
not be published, broadcast, rewritten or redistributed.
Thompson Reuters is solely responsible for this content.

|
|